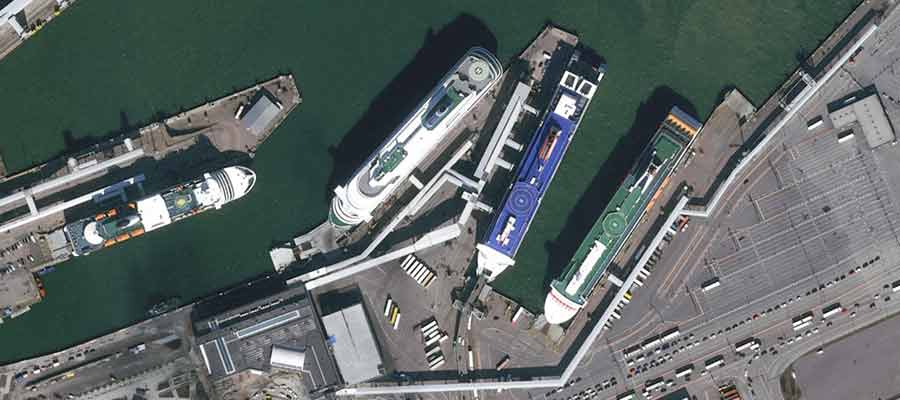
30cm native resolution Pléiades Neo image over port in Tallinn, Estonia
Airbus Intelligence provides users with access to satellite imagery, innovative geospatial analytics, and industry-specific insights. Image data from the Airbus Constellation of satellites, which includes twin SPOT 6/7, Vision-1, Pléiades, and Pléiades Neo satellites are used to deliver actionable intelligence to a variety of markets around the globe.
Already known for quick processing and delivery of imagery and derived products, the Airbus processing workflow is now even faster – just a few hours after satellite acquisition in many cases – thanks to cloud technology.
In preparation for the Pléiades Neo era, Airbus redesigned its ground segment, moving Pléiades Neo, Pléiades and SPOT optical image archiving and processing to the cloud. This essentially connects the satellites directly to the cloud where raw imagery is ready for real-time processing of orders placed from anywhere in the world.
New and archived satellite imagery in a variety of processing levels, as well as elevation data, 3D models, and other global data sets are available to customers through the automated OneAtlas platform or

The OneAtlas Platform showing 30cm Pléiades Neo data over Dubai
through customer service. These products can be delivered via streaming, download, and API in multiple formats for easy integration into your GIS workflows. The Airbus Intelligence optical imagery catalog encompasses the full Pléiades (50cm), SPOT 6/7 (1.5m) and Pléiades Neo (30cm) data sets now and will include data from Vision-1 (87cm) soon.
For online OneAtlas users, curated cloud-free data are added daily to the easily searchable, subscription based Living Library, while all images dating back to 2012 are available in the Extended Archive. Customer Service users may call or email a representative for assistance selecting the data set that best fits their needs.
While these technical improvements have elevated Airbus optical satellites to the pinnacle of Earth observation with Pléiades Neo, the ground segment has been continually augmented as well. From acquisition tasking to image processing and product creation to delivery, the entire production chain has been upgraded and streamlined with cloud technology to deliver high-quality image products quickly and efficiently to customers.
Online Customer Tasking
Airbus was the first to offer customers with flexible tasking options. For decades, users have been able to schedule image acquisitions over their areas of interest days, weeks or months in advance. Their selections have been supplemented with latest weather forecasts and automated notifications that allow the user to be informed at each step of their new collection request and to cancel a scheduled collect for a specific day less than 24 hours before hand if cloudy or other poor conditions imperil capture of a quality image.
Today, Airbus has put Tasking orders directly into the hands of end users. Through the intuitive OneAtlas interface, customers may schedule image acquisitions by any of the four optical constellations. Users can select their own tasking parameters and processing options, generally allowing an acquisition order to be placed 24 hours in advance. However, Airbus is now proud to announce the new Pléiades Neo satellites can be scheduled by the user to capture an image in as little as 25 minutes before the satellite passes over a specific AOI. This direct, short-notice Tasking is ideal for monitoring natural disasters, emergencies, and other rapidly evolving events that have occurred unexpectedly.
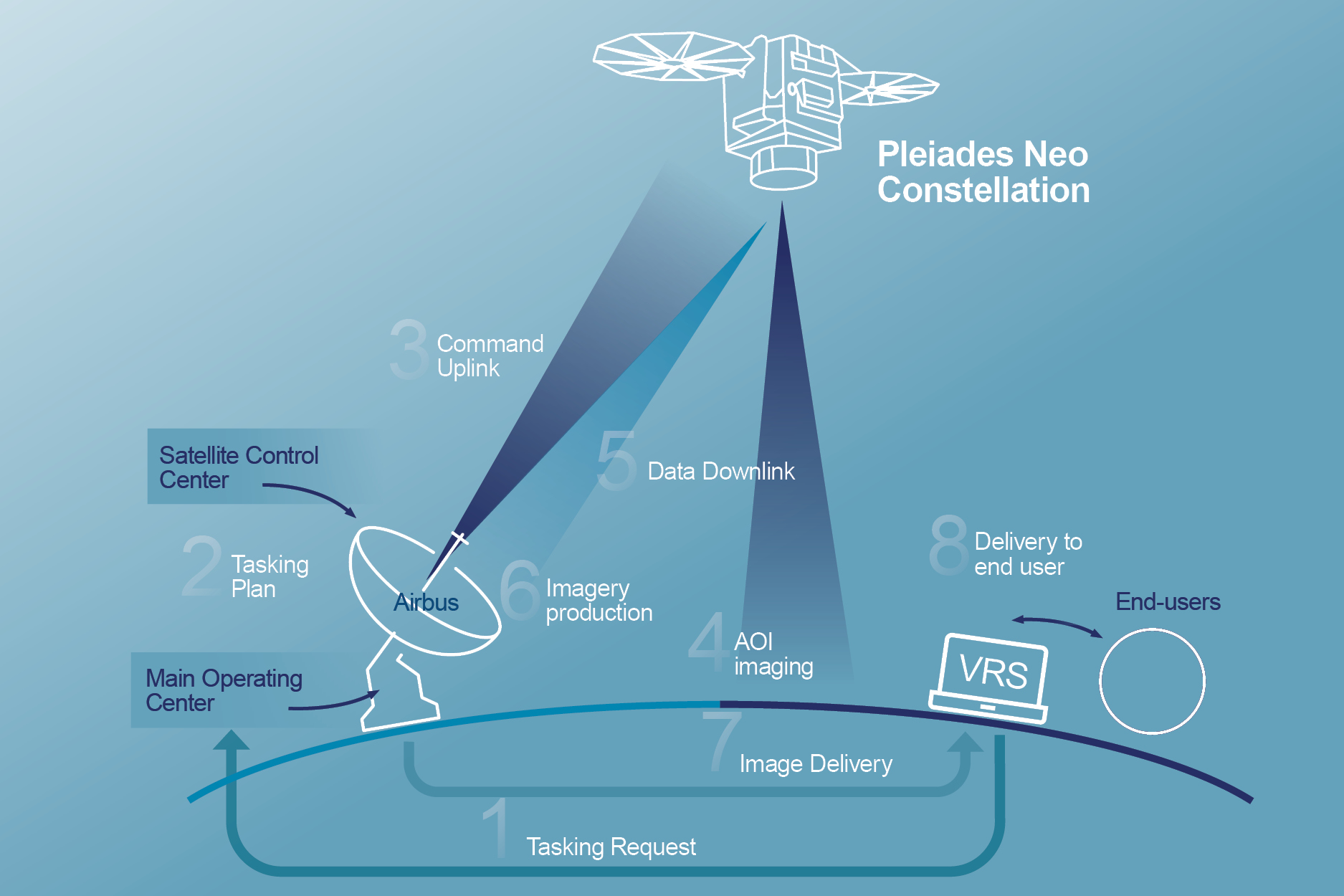
The Tasking process from Pléiades Neo to rapidly task, acquire and process the data for easy access into OneAltas
Optical Image Processing Options
Pansharpening
Pansharpening is the most common image processing technique applied to Airbus optical satellite data. Each of the four optical constellations captures imagery in a single relatively wide visible band, called Panchromatic, at high or very high spatial resolution. In addition, each sensor captures multispectral data in several narrower discrete wavelengths in visible (RGB) and near-infrared portions of the spectrum at slightly coarser spatial resolution.
Geometric Correction
Airbus offers three levels of processing to remove geometric distortions from satellite images: Primary, Projected, and Orthorectification. The objective of geometric processing is to improve the geolocation accuracy of x, y, and z points measured in the imagery. Although all imaging sensors rely on onboard sensors, star trackers, and inertial measurement units to geolocate image pixels, some additional processing must occur on the ground to further improve the overall geometric accuracy.
In preparation for the Pléiades Neo constellation, Airbus developed an entirely new global reference database to geometrically correct images acquired by any optical sensor. This database, called Space Reference Points (SRP), contains a worldwide network of 3D ground control points generated by performing a bundle adjustment on the SPOT 6/7 multiview archive. The accuracy of this new SRP database, used extensively in orthorectification processes, has improved standard geometric correction on Airbus products, up to < 5m CE90.
The new SRP database is important because it is now used to geometrically correct all Airbus optical image products. Of critical importance, images from Pléiades Neo, twin Pléiades satellites , SPOT 6/7, and Vision-1 can be aligned to the same reference system, which means they are fully compatible with each other for large, multi-sensor analysis projects, such as time-series change detection. Intersensor compatibility is a requirement for analysis involving Artificial Intelligence. Three levels of Geometric Correction are available:
- Primary: Also known as System-Ready, Primary Processing is geometrically very close to the raw image data received from the satellite sensor. These data sets are meant for customers who will perform their own orthorectification or digital elevation model (DEM) creation. Customers receive the sensor model and RPCs to use in performing bundle adjustments and making their own corrections to the data.
- Projected: Referred to as View-Ready, Projected images are mapped on the Earth with a standard reference datum and projection system at a fixed terrestrial altitude. The Default is WGS84/UTM. Like the Primary data sets, Projected images are delivered with sensor models and RPCs for users performing orthorectification with their own GCPs or DEMs. The main advantage of Projected images is they are compatible with GIS environments.
- Orthorectification: Sometimes called Map-Ready or Analysis Ready products, Orthorectified images have had geometric distortions removed so the final image has the georeferenced qualities of a map. Airbus applies an automated orthorectification process that uses the new SRP database to remove horizontal and vertical distortions from the data. Customers ordering orthorectified products may also select from two relief models to project the image onto for proper display of the terrain. The most popular is the SRTM (Shuttle Radar Topography Mission) which is a very smooth data set ideal for nadir images with minimal terrain distortions. The other option is the WorldDEM, which provides more accuracy and is better suited for off-nadir images that experience significant terrain distortion caused by the angle of image acquisition.
Airbus offers additional radiometric processing options and delivery formats for satellite imagery that are based on customers’ needs and applications.
To learn more about OneAtlas, please visit our website, or download more information about our processing and imagery delivery formats here.